If you've been anywhere near the tech world lately, you've probably heard people tossing around terms like 'LLM' and 'Generative AI' as if they're the same thing. This confusion isn't just a minor annoyance – it's actually holding back tech enthusiasts, businesses, and developers from making the most of these powerful technologies. Think of Generative AI as a vast creative studio that can produce new content across every medium imaginable, while LLMs are the master wordsmiths within that ecosystem, specializing in understanding and generating text with remarkable sophistication.
As organizations increasingly explore custom LLMs tailored to their specific industry needs and data requirements. Throughout this blog, we'll explore the key distinctions between these technologies, examine their real-world applications, and look ahead to future trends. By the end, you'll have a clear understanding of generative artificial intelligence in all its forms, and more importantly, you'll know exactly which approach makes sense for your specific goals.
What is Generative AI?
Generative AI represents a category of AI systems with a unique superpower: creating completely new content. These systems learn patterns from existing data to generate something that never existed before. This sets generative AI apart from traditional AI which focuses on analyzing or classifying data. Instead of processing what exists, Generative AI acts as a creative partner, producing fresh outputs: text, images, videos, code and audio. Behind the scenes it leverages advanced neural networks like GANs and diffusion models that teach machines to mimic human creativity. The result is AI that doesn't just understand patterns but uses them to create something new.
Generative AI trains on massive datasets to predict and produce new creations. Tools like Flux and Midjourney generate images from text descriptions while MusicGen creates original music. The technology has exploded in popularity across entertainment and marketing and design. Investments reached $33.9 billion globally in 2024.
The technology's strength lies in its multimodality that handles diverse inputs and outputs. You can input a sketch and get a polished video or combine text with audio for personalized podcasts. However challenges persist including data biases and ethical concerns. These models can replicate harmful stereotypes from their training data. Generative AI democratizes creativity by enabling non-experts to produce high-quality content efficiently.
What is a Large Language Model (LLM)?
A Large Language Model (LLM) is a type of artificial intelligence model that has been developed to process, interpret, and generate human-like text. LLMs rely on deep learning architectures, particularly transformers, and are pre-trained on a massive corpora of text data—literally billions of words of text from books, websites, and articles—to predict the next word in a sequence. This creates an inherent fluency in tasks such as summarization, translation, and conversation.
Some familiar examples of LLMs include OpenAI's GPT-5, Anthropic's Claude, Meta's Llama series, Google's Gemini, and xAI's Grok 4. These models excel in natural language processing (NLP), making them ideal for chatbots, content writing and code generation. GPT-5 allows you to write emails or respond to prompts, to more utility by pulling a function out of a prompt in python code!
LLMs represent a pinnacle of language-focused AI, with parameters often exceeding hundreds of billions, allowing for nuanced context understanding. However, LLMs are focused mainly on text which limits their functionality compared to broader AI systems. In 2025, open-sources like Llama 4, first began to hit the mainstream, thus expanding accessibility and customization. Despite their power, LLMs face issues like hallucinations—generating plausible but incorrect information and high computational demands.
Key Differences Between LLM & Generative AI
While LLMs are a form of Generative AI, the differences between LLM and Generative AI are significant in scope, functionality, and application. Generative AI is an umbrella term for any AI that creates new content across modalities, whereas LLMs are specifically tailored for language tasks.
Here's a detailed AI models comparison:
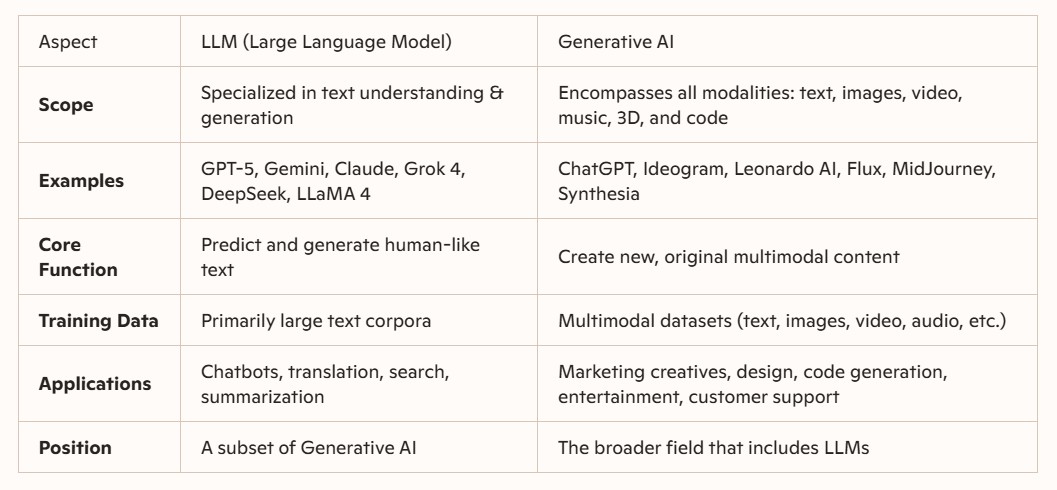
In terms of use cases, Generative AI shines in creative industries like generating artwork or videos while LLMs dominate in text-heavy domains such as legal drafting or customer support. The key takeaway? All LLMs are Generative AI but not all Generative AI is an LLM.
Similarities Between LLM & Generative AI
Despite the differences, LLM and Generative AI share foundational principles. Both rely on machine learning to generate novel outputs from learned patterns, using large datasets for training. They employ probabilistic methods to create content that's contextually relevant and human-like. Ethical challenges such as data privacy and bias mitigation, apply to both, as do advancements in efficiency through techniques like fine-tuning. In hybrid applications, LLMs often integrate with Generative AI for enhanced multimodal experiences like voice-assisted chatbots.
Real-World Applications and Use Cases
Generative AI's applications are vast: in healthcare, it aids in drug discovery by simulating molecular structures; in entertainment, tools like Stable Diffusion create custom visuals. On the other hand, LLMs power virtual assistants (e.g., ChatGPT for queries), automate coding (GitHub Copilot) and enhance education through personalized tutoring.
For businesses, choosing between them depends on needs—use Generative AI for multimedia campaigns and LLMs for content marketing or SEO optimization.
The combination of LLMs and generative AI is transforming industries across the board:
- E-commerce:
- Personalized product recommendations
- Dynamic product descriptions
- AI-generated product images
- Customer service chatbots
- Content Creation:
- Blog post generation and optimization
- Social media content creation
- Video script writing
- Image and graphics generation
- Healthcare:
- Medical documentation and summarization
- Patient communication tools
- Medical imaging analysis
- Drug discovery research
- Education:
- Personalized learning materials
- Language translation tools
- Interactive tutoring systems
- Content summarization for research
Future Trends in LLM & Generative AI
Looking ahead, 2025 promises exciting developments. Multimodal integration will blur lines, with LLMs evolving into agentic AI systems that act autonomously. Open-source models will democratize access, while ethical AI and sustainability focus on reducing energy consumption. Investments in Generative AI are projected to boost global GDP by 7%, with trends like hyper-personalization and dynamic model selection leading the way.
Conclusion
In the LLM vs Generative AI debate, the real value lies in their complementary strengths. Generative AI offers boundless creativity across formats while LLMs provide precise language mastery. By understanding the differences between the two, you can use the most appropriate tool for innovation. As AI develops, understanding generative artificial intelligence and large language models will be vital. Ready to implement? Explore these technologies today and transform your workflow.





